Yes, taking Cipro (ciprofloxacin) can lead to a yeast infection. This antibiotic works by disrupting the growth of bacteria, but it can also affect the balance of normal flora in the body. When antibiotics eliminate beneficial bacteria, it creates an environment where yeast can thrive, resulting in an infection.
If you notice symptoms such as itching, burning, or unusual discharge during or after a course of Cipro, consult your healthcare provider. They may recommend antifungal treatments to address the yeast infection. It’s also wise to ask about probiotic options, which can help restore the natural balance of bacteria in your system.
To minimize the risk of developing a yeast infection while on Cipro, maintain good hygiene and consider incorporating probiotic-rich foods into your diet, such as yogurt or kefir. Staying hydrated and avoiding excessively sugary foods can also support your body in preventing yeast overgrowth.
- Can Cipro Cause Yeast Infection?
- Understanding Cipro and Its Uses
- How Antibiotics Affect Body Microflora
- Cipro and Its Mechanism of Action
- Targeting Bacterial Infections
- Absorption and Distribution
- Link Between Antibiotics and Yeast Infections
- Understanding the Connection
- Preventive Measures
- Symptoms of Yeast Infections
- Physical Signs
- Less Common Symptoms
- Risk Factors for Developing Yeast Infections on Cipro
- Preventive Measures While Taking Cipro
- Alternative Treatments to Consider
- When to Consult a Healthcare Professional
- Recognize Warning Signs
- Discuss Medication and Symptoms
Can Cipro Cause Yeast Infection?
Yes, Cipro (ciprofloxacin) can lead to a yeast infection as a side effect. Antibiotics like Cipro disrupt the natural balance of bacteria in the body, including in the vaginal area. This imbalance allows for the overgrowth of yeast, which can result in an infection.
If you are taking Cipro and notice symptoms such as itching, burning, or unusual discharge, consult your healthcare provider. They can confirm if it’s a yeast infection and provide appropriate treatment. Maintaining good hygiene, wearing breathable fabrics, and consuming probiotics can help mitigate this risk while on antibiotics.
| Symptoms of Yeast Infection | Recommended Actions |
|---|---|
| Itching | Consult your doctor |
| Burning sensation | Consider over-the-counter antifungal treatments |
| Unusual discharge | Schedule an appointment |
Taking steps to prevent a yeast infection while using Cipro can make your treatment safer and more comfortable. Proper dialogue with your healthcare provider is essential for effectively managing any side effects.
Understanding Cipro and Its Uses
Cipro, or ciprofloxacin, is an antibiotic in the fluoroquinolone class, primarily used to treat bacterial infections. It effectively targets various conditions, including urinary tract infections, respiratory infections, and certain types of gastroenteritis. Cipro works by inhibiting the bacteria’s ability to replicate, thereby halting the infection’s progression.
This medication is often prescribed for infections caused by specific bacteria, such as Escherichia coli and Salmonella. When taking Cipro, adhere to the prescribed dosage and complete the entire course, even if symptoms improve, to prevent the development of antibiotic resistance.
Patients should stay hydrated while on Cipro, as the medication can impact kidney function. Some users report side effects like nausea or dizziness; these usually subside after a few days. Monitoring for more severe reactions, particularly tendon pain or swelling, is important, as these can indicate rare but serious side effects.
Cipro can alter the natural balance of bacteria in the body, potentially leading to opportunistic infections, such as yeast infections. This occurs because, while Cipro targets harmful bacteria, it may also affect beneficial bacteria, paving the way for yeast overgrowth.
To mitigate the risk of yeast infections, consider incorporating probiotics into your routine during and after Cipro treatment. Probiotics can help restore healthy bacteria levels in the body. If symptoms of a yeast infection do occur, consult a healthcare provider for appropriate treatment options.
How Antibiotics Affect Body Microflora
Antibiotics disrupt the balance of the body’s microflora, targeting harmful bacteria but also affecting beneficial strains. This can lead to an overgrowth of yeast, resulting in infections such as candidiasis. Researchers have shown that antibiotics can reduce the diversity of the gut microbiome, making it less resilient to colonization by unwanted organisms.
Taking antibiotics without a prescription or proper guidance increases the risk of microflora imbalances. It’s advisable to consult a healthcare provider before starting any antibiotic treatment. Consider probiotics as a preventive measure; these supplements help restore beneficial bacteria during and after antibiotic use.
Diet plays a significant role in maintaining healthy microflora. Incorporate fermented foods like yogurt, kefir, and sauerkraut into your meals. These foods provide natural sources of probiotics that support the growth of beneficial bacteria.
Stay hydrated and consume a diet rich in fiber, as it nourishes gut bacteria. Foods high in prebiotics, such as garlic, onions, and bananas, promote the growth of beneficial microorganisms, helping to restore balance.
Lastly, monitor your health for any signs of yeast infections after antibiotic treatment. Symptoms like unusual discharge or irritation warrant a consultation with a healthcare professional. Early intervention can restore balance more effectively.
Cipro and Its Mechanism of Action
Cipro, or ciprofloxacin, belongs to the fluoroquinolone class of antibiotics. It works by inhibiting bacterial DNA gyrase and topoisomerase IV, enzymes critical for DNA replication and repair. By disrupting these enzymes, Cipro effectively halts bacterial growth and reproduction.
Targeting Bacterial Infections
This antibiotic is particularly effective against a variety of gram-negative and some gram-positive bacteria. Cipro is commonly prescribed for conditions such as urinary tract infections, respiratory infections, and skin infections. The inhibition of DNA synthesis leads to the death of susceptible bacteria, thereby clearing the infection.
Absorption and Distribution
Cipro achieves high bioavailability when taken orally, allowing it to reach therapeutic levels in the bloodstream. It distributes well throughout the body, including penetration into tissues such as the lungs and urinary tract. For optimal results, it is recommended to stay adequately hydrated while taking Cipro, as this can help the medication’s effectiveness and minimize potential side effects.
Always follow your healthcare provider’s instructions regarding dosage and duration of treatment to ensure the best outcome and reduce the risk of antibiotic resistance.
Link Between Antibiotics and Yeast Infections
Antibiotics can disrupt the natural balance of bacteria in the body, leading to an overgrowth of yeast. This shift often results in yeast infections, especially in individuals using broad-spectrum antibiotics.
Understanding the Connection
Antibiotics target harmful bacteria but also affect beneficial bacteria that typically help control yeast levels. The loss of these protective bacteria allows yeast, particularly Candida, to thrive. Certain antibiotics, like ciprofloxacin, can significantly alter this balance, increasing the risk of infections.
Preventive Measures
To minimize the likelihood of a yeast infection while taking antibiotics, consider these strategies:
- Probiotics: Incorporate probiotic-rich foods, such as yogurt and kefir, or take probiotic supplements to support healthy bacteria levels.
- Hydration: Drink plenty of water to help flush out toxins from the body.
- Symptoms Awareness: Be alert for early signs of yeast infections, including itching, unusual discharge, and irritation. Consult a healthcare professional if symptoms arise.
- Follow Prescriptions: Complete the full course of antibiotics to prevent resistance but consult a doctor if concerned about side effects.
Maintaining a healthy lifestyle and monitoring your body’s response during antibiotic treatment can further reduce the risk of yeast infections.
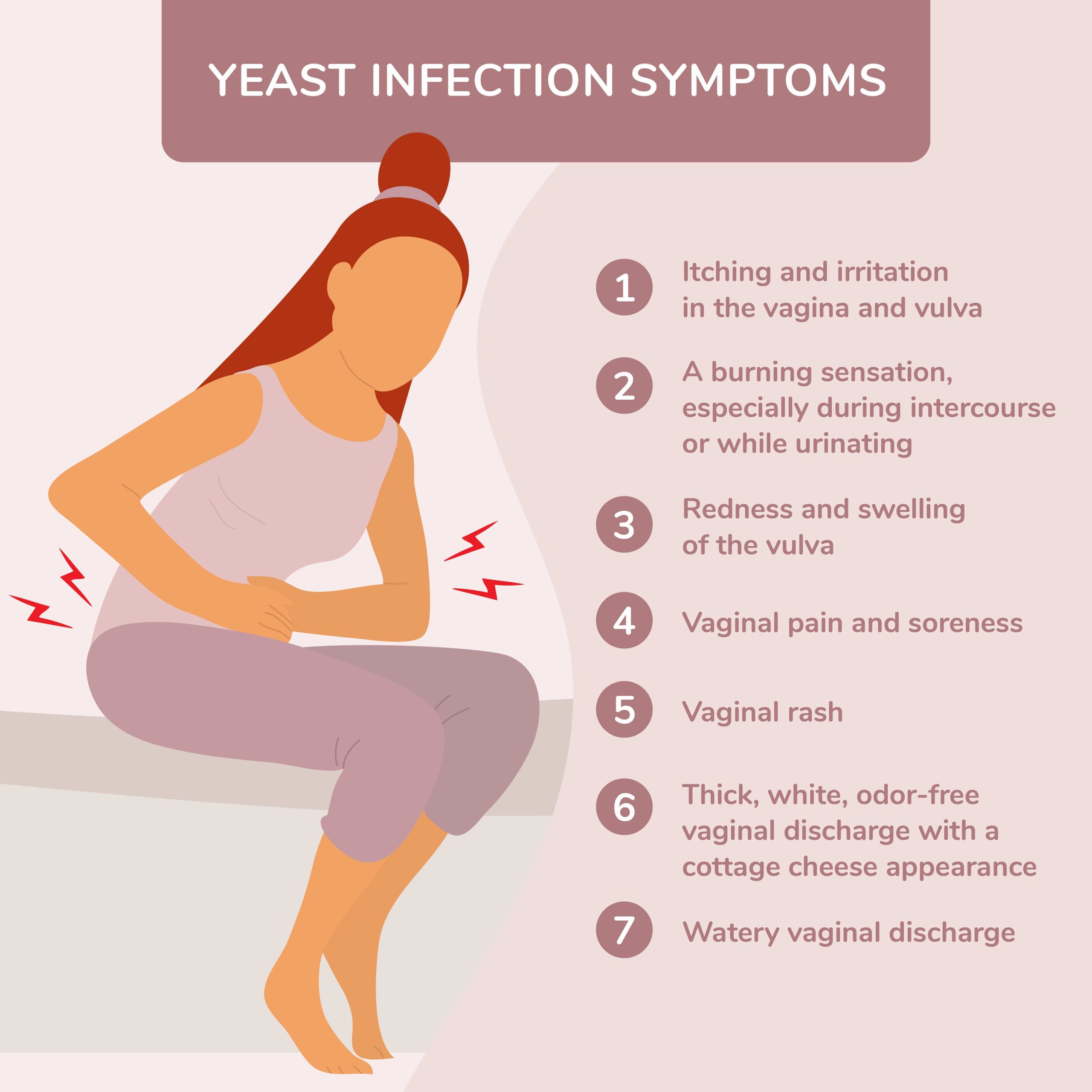
Symptoms of Yeast Infections
Recognizing the symptoms of a yeast infection can lead to timely treatment and relief. The most common symptom is itching in the affected area, which can be quite intense and persistent. This discomfort often exacerbates during the evening or after sexual intercourse.
Physical Signs
Observe for a thick, white discharge that resembles cottage cheese. This discharge typically does not have a strong odor. Redness and swelling of the vulva and vagina are also frequent indicators. Some individuals may experience soreness or irritation, particularly during urination or intercourse.
Less Common Symptoms
In some cases, yeast infections can cause abdominal pain or general discomfort. If you experience recurring yeast infections, consider consulting a healthcare provider, as this could indicate an underlying condition. Keep track of your symptoms to share with your doctor for better management.
Risk Factors for Developing Yeast Infections on Cipro
Taking ciprofloxacin (Cipro) increases the likelihood of yeast infections due to its impact on the body’s natural bacterial balance. Here are specific risk factors to consider:
- Long-term Use: Prolonged courses of Cipro can significantly disrupt the gut flora, allowing yeast to proliferate.
- Previous Yeast Infections: A history of yeast infections can indicate a susceptibility when antibiotics like Cipro are used.
- Weak Immune System: Individuals with compromised immune systems, whether from disease or medication, face a higher risk of developing infections.
- Diabetes: High blood sugar levels can foster yeast growth, making diabetic patients especially vulnerable during antibiotic treatment.
- Hormonal Changes: Fluctuations in hormones, such as those occurring during menstruation or pregnancy, can predispose individuals to yeast infections while on antibiotics.
- Inadequate Hygiene: Poor hygiene practices can exacerbate the risk, creating an environment conducive to yeast growth.
- Use of Contraceptives: Certain hormonal contraceptives can affect the vaginal flora, potentially increasing risk when combined with antibiotics.
To mitigate these risks, maintain good hygiene, consider probiotics, and consult a healthcare provider if symptoms of a yeast infection arise during or after taking Cipro.
Preventive Measures While Taking Cipro
Stay hydrated by drinking plenty of water throughout the day. This helps to flush out bacteria and supports your overall health.
Incorporate probiotics into your diet. Foods like yogurt, kefir, and fermented vegetables can help maintain a healthy balance of bacteria in your body, potentially reducing the risk of yeast infections.
Practice good hygiene. Keep your genital area clean and dry, as moisture can encourage yeast growth. Opt for breathable cotton underwear to promote ventilation.
Limit sugar intake. High sugar consumption can contribute to the overgrowth of yeast, so moderating sweets and refined carbohydrates can be beneficial.
Monitor for symptoms. Pay attention to any signs of irritation or imbalance and consult your healthcare provider promptly if you notice any unusual changes.
Avoid unnecessary antibiotics. Only take Cipro when prescribed. Reducing other antibiotics can help preserve your body’s natural flora.
Consider discussing with your doctor the option of antifungal medications if you have a history of yeast infections. Being proactive can prevent future complications.
Alternative Treatments to Consider
Probiotics serve as a powerful ally in preventing yeast infections, particularly after antibiotic use like ciprofloxacin. These beneficial bacteria help restore the natural balance of flora in the body. Look for high-quality probiotic supplements or consider incorporating fermented foods such as yogurt, kefir, sauerkraut, and kimchi into your diet.
Garlic offers another natural remedy due to its antifungal properties. Incorporating raw garlic into your meals or taking garlic supplements may help combat yeast overgrowth. You can also explore topical applications of diluted garlic oil, but ensure to do a patch test for any skin sensitivity.
Coconut oil is celebrated for its antifungal effects. Applying organic coconut oil to affected areas can soothe irritation while working against yeast. Consuming it as part of a balanced diet can also offer internal benefits.
Tea tree oil, known for its antimicrobial properties, may provide relief when used in a diluted form. Adding a few drops to a carrier oil and applying it sparingly can help manage symptoms. Ensure the solution is well-diluted to avoid skin irritation.
A conscientious approach to diet can support your body’s defenses. Reduce sugar intake as yeast thrives on sugar, while focusing on whole foods, including vegetables, lean proteins, and whole grains, can bolster immune function. Staying hydrated and avoiding excessive alcohol also plays a role in maintaining balance.
Stress management techniques such as mindfulness, yoga, and regular exercise can bolster your immune health. These practices enhance overall well-being, making your body more resilient against infections.
Always consult with a healthcare professional before starting any new treatment approach, especially when dealing with infections. Each individual’s health needs differ, and tailored guidance can optimize your strategy.
When to Consult a Healthcare Professional
If you experience symptoms of a yeast infection while taking Cipro, seek medical advice. Symptoms may include itching, burning, and unusual discharge. Addressing these signs early can help prevent complications and promote faster recovery.
Recognize Warning Signs
- Persistent itching or irritation in the genital area.
- Redness and swelling of the vulva or surrounding areas.
- Unusual discharge that has an abnormal color or odor.
- Discomfort during intercourse or urination.
Discuss Medication and Symptoms
If you suspect that Cipro is causing these symptoms, inform your healthcare provider. They can evaluate your condition, determine possible links to the medication, and suggest appropriate treatments. Always mention any other medications you are taking or any allergies you may have to ensure safe and effective care.