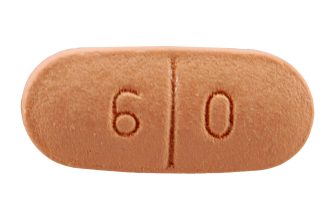
Consider introducing Pravastatin sodium 40 mg into your daily routine if you’re looking to manage your cholesterol levels effectively. This medication belongs to a class of drugs known as statins, which help reduce the amount of cholesterol your body produces. By lowering LDL cholesterol, or “bad” cholesterol, pravastatin can significantly decrease the risk of heart disease and stroke.
For optimal results, take the tablet with or without food, but aim to do so at the same time each day. Consistency enhances its cholesterol-lowering benefits. Regular monitoring of your cholesterol levels allows you to track your progress and make necessary adjustments with your healthcare provider.
Be aware of potential side effects, which, while generally mild, can include headache, nausea, and muscle pain. If you experience severe reactions such as unusual fatigue or difficulty breathing, seek medical attention immediately. Maintaining open communication with your healthcare team ensures any concerns are addressed and your treatment can be adjusted as needed.
Incorporating lifestyle changes, such as adopting a balanced diet and engaging in regular exercise, can complement the effectiveness of pravastatin. These actions not only support your health but also enhance the overall efficacy of the medication. Stay proactive about your cardiovascular health for long-term benefits.
- Detailed Information on Pravastatin Sodium 40 mg Tabs
- Mechanism of Action
- Dosage and Administration
- Chemical Composition and Mechanism of Action of Pravastatin
- Indications for Use of Pravastatin Sodium 40 mg
- Dosage Guidelines and Administration Recommendations
- Potential Side Effects and Contraindications
- Serious Side Effects
- Contraindications
- Drug Interactions and Precautions for Pravastatin Use
- Precautions and Monitoring
- Dietary Considerations
Detailed Information on Pravastatin Sodium 40 mg Tabs
Pravastatin sodium 40 mg tablets serve as a targeted approach to managing cholesterol levels. This medication is primarily used to lower low-density lipoprotein (LDL) cholesterol and triglycerides while increasing high-density lipoprotein (HDL) cholesterol. Patients with hyperlipidemia or a high risk of cardiovascular diseases benefit significantly from this treatment.
Mechanism of Action
Pravastatin inhibits HMG-CoA reductase, an enzyme critical to the cholesterol biosynthesis pathway. By blocking this enzyme, pravastatin effectively reduces the body’s cholesterol production. This leads to a decrease in overall cholesterol levels in the bloodstream and promotes the utilization of existing cholesterol, aiding in cardiovascular health.
Dosage and Administration
The standard dose is typically 40 mg taken once daily. It can be administered at any time of day, with or without food. Routine monitoring of lipid levels is advisable to assess effectiveness and adjust the dosage if necessary. Patients should adhere strictly to their healthcare provider’s instructions for optimizing treatment outcomes.
Possible side effects include headache, nausea, and muscle pain. Severe reactions, although rare, may include liver damage or rhabdomyolysis. Regular liver function tests can help mitigate risks.
Consult with a healthcare professional regarding any existing medications, as interactions may occur. Combining pravastatin with certain drugs can increase the risk of severe side effects.
Incorporating lifestyle changes such as a balanced diet and regular exercise further enhances the benefits of pravastatin. Engage in these practices alongside medication for a holistic approach to heart health.
Chemical Composition and Mechanism of Action of Pravastatin
Pravastatin is a member of the statin class of drugs, specifically designed to lower cholesterol levels in the blood. Its chemical name is (E)-(3R, 5R)-7-[2-(4-fluorophenyl)-4-methyl-1H-imidazol-1-yl]-3,5-dihydroxyhept-6-enoic acid. The molecular formula is C23H35NaO7, featuring a sodium salt form that enhances solubility.
The primary mechanism of action revolves around the inhibition of HMG-CoA reductase, an enzyme crucial for cholesterol biosynthesis in the liver. By blocking this enzyme, pravastatin effectively reduces the hepatic synthesis of cholesterol, leading to a corresponding decrease in low-density lipoprotein (LDL) levels in the bloodstream.
Key steps in pravastatin’s action include:
- Reduction of cholesterol production in the liver.
- Increase in hepatic uptake of circulating LDL cholesterol.
- Enhancement of high-density lipoprotein (HDL) cholesterol levels.
- Decreased production of apolipoprotein B, which is a primary component of LDL.
Pravastatin also exhibits pleiotropic effects, which include reducing inflammation and improving endothelial function, thus contributing to cardiovascular health beyond its lipid-lowering capabilities.
For optimal results, dosing can vary, but a typical starting dose is 40 mg daily, adjusted based on individual response and clinical goals. Regular monitoring of lipid levels and liver function tests is advised to ensure safety and efficacy throughout the treatment process.
Indications for Use of Pravastatin Sodium 40 mg
Pravastatin sodium 40 mg is primarily prescribed to reduce cholesterol levels in adults with hyperlipidemia. It specifically targets low-density lipoprotein (LDL) cholesterol, effectively lowering it and helping to manage overall lipids.
This medication is indicated for the prevention of cardiovascular disease in patients with risk factors such as hypertension, diabetes, and family history of heart disease. By lowering LDL cholesterol and total cholesterol, pravastatin aids in reducing the risk of heart attacks and strokes.
Patients with established atherosclerotic cardiovascular disease (ASCVD) may also benefit from this statin, as it contributes to the stabilization of plaque and decreases the likelihood of heart-related events.
Additionally, pravastatin is helpful for patients with genetic disorders that lead to high cholesterol levels, such as familial hypercholesterolemia. In these cases, it serves as part of a comprehensive treatment strategy that may include dietary changes and other medications.
Monitoring lipid levels periodically during treatment ensures that pravastatin remains effective, making necessary adjustments or additional therapies as needed. Always consult a healthcare professional for personalized recommendations and management plans.
Dosage Guidelines and Administration Recommendations
Start treatment with Pravastatin sodium at a dosage of 40 mg once daily. It is recommended to take the tablet in the evening to align with the body’s natural cholesterol synthesis rhythm.
In certain cases, healthcare providers may adjust the dose based on the individual’s cholesterol levels and response to therapy. Regular monitoring of lipid levels is crucial for determining the appropriate adjustments.
| Patient Population | Initial Dose | Dosage Adjustments |
|---|---|---|
| Adults | 40 mg once daily | Monitor lipid levels after 4-12 weeks; adjust if necessary. |
| Patients with Renal Impairment | Starting dose may be reduced to 20 mg once daily. | Consult with a healthcare professional for individualized titration. |
| Geriatric Patients | 40 mg once daily | Evaluate for potential need for reduced dose based on tolerance. |
Take Pravastatin with or without food, ensuring consistent use at the same time each day for optimal effects. Encourage patients to maintain a heart-healthy diet, as it enhances the drug’s benefits.
Do not abruptly discontinue Pravastatin without consulting a healthcare provider, as this may lead to adverse effects on cholesterol levels. If a dose is missed, take it as soon as remembered. If the next dose is near, skip the missed dose and resume the regular schedule. Do not double doses.
Patients should report any unusual symptoms, such as muscle pain or weakness, and discuss any concurrent medications with their healthcare provider to avoid potential interactions.
Potential Side Effects and Contraindications
Take note of the potential side effects when using Pravastatin sodium 40 mg tabs. Common reactions include headache, dizziness, and gastrointestinal disturbances such as nausea and diarrhea. Muscle pain or weakness may occur, which can signal a rare but serious condition called rhabdomyolysis. Contact a healthcare provider if you experience unusual muscle discomfort, tenderness, or dark-colored urine.
Serious Side Effects
Some individuals may encounter liver issues, signified by symptoms such as yellowing of the skin or eyes, abdominal pain, and fatigue. Regular liver function tests can help monitor any changes during treatment. Ensure to discuss any existing liver conditions with your healthcare provider before starting the medication.
Contraindications
Avoid using Pravastatin if you are allergic to it or any of its components. Pregnant or breastfeeding women should not take this medication due to potential risks to the fetus or infant. Individuals with active liver disease or severe renal impairment should consider alternative treatments. Always inform your healthcare provider about any other medications or supplements you are currently taking to prevent interactions.
Drug Interactions and Precautions for Pravastatin Use
Pravastatin may interact with several medications, altering its effectiveness or increasing the risk of side effects. Notably, cyclosporine can raise pravastatin levels in the blood, requiring dosage adjustments. Antibiotics such as erythromycin and azithromycin may also enhance the effects of pravastatin, necessitating careful monitoring. Additionally, gemfibrozil significantly increases the risk of myopathy; co-administration should generally be avoided.
Staying informed about your medication regimen is essential. Always inform your healthcare provider about all medications, supplements, and herbs you are taking. This information helps mitigate potential interactions. Regular liver function tests are recommended to monitor your liver health, especially if you have a history of liver disease or alcohol use. Pregnant or breastfeeding women should refrain from using pravastatin due to potential risks to the fetus or infant.
Precautions and Monitoring
Those with a history of muscle disorders or significant thyroid problems should use pravastatin cautiously. Be alert to any unusual muscle pain or weakness, as these symptoms may indicate serious side effects. Combine lifestyle changes, such as a healthy diet and exercise, with pravastatin use for optimal cholesterol management. Regular follow-ups with your healthcare provider will ensure effective treatment and help address any concerns that arise during your therapy.
Dietary Considerations
Avoid grapefruit and grapefruit juice while taking pravastatin. These can increase the level of the drug in your bloodstream, leading to higher risks of side effects. Maintain a balanced diet, focusing on reducing saturated fats and cholesterol intake to enhance the medication’s effectiveness.